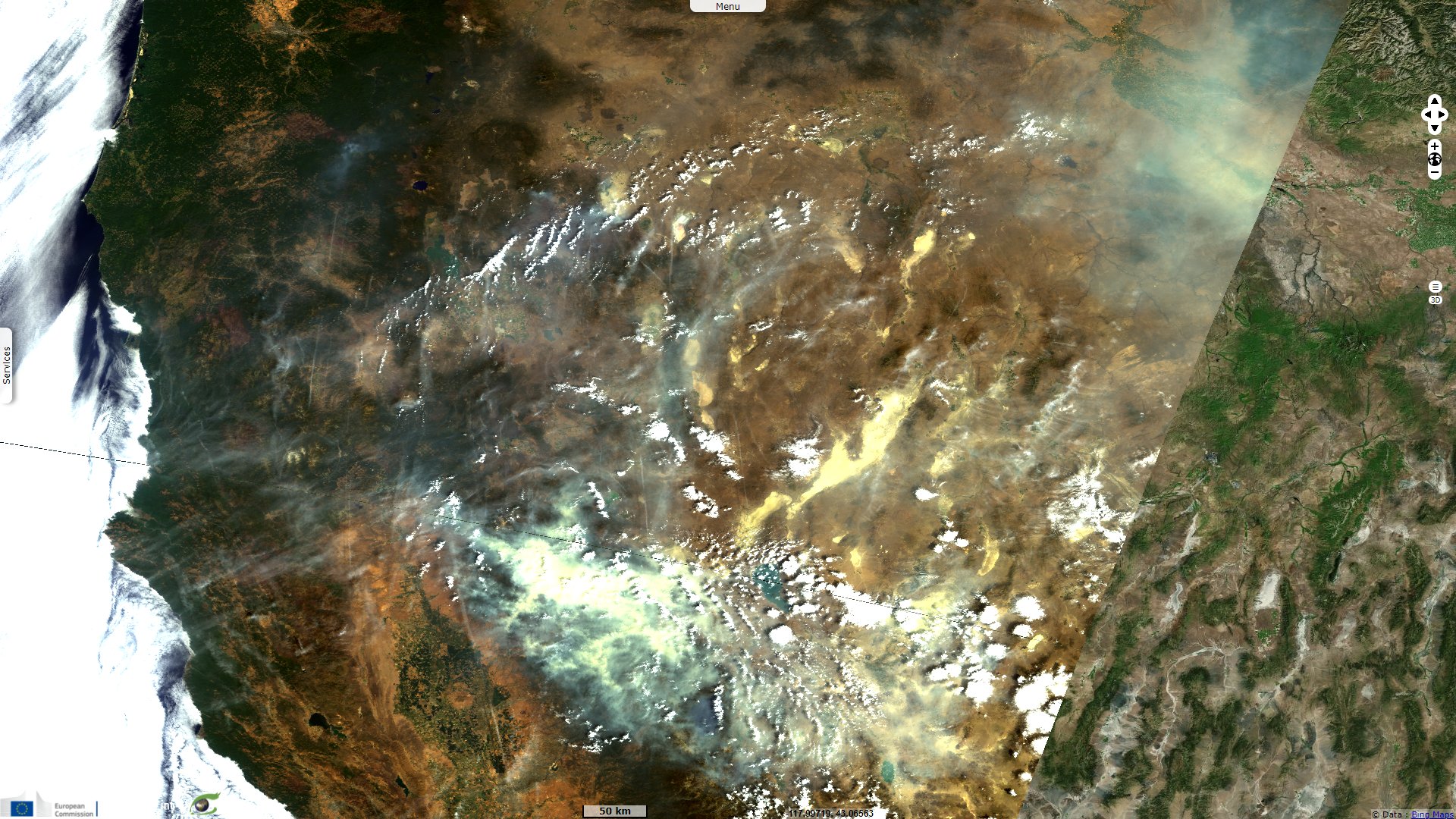
Wildfires bathe California in smoke, United States
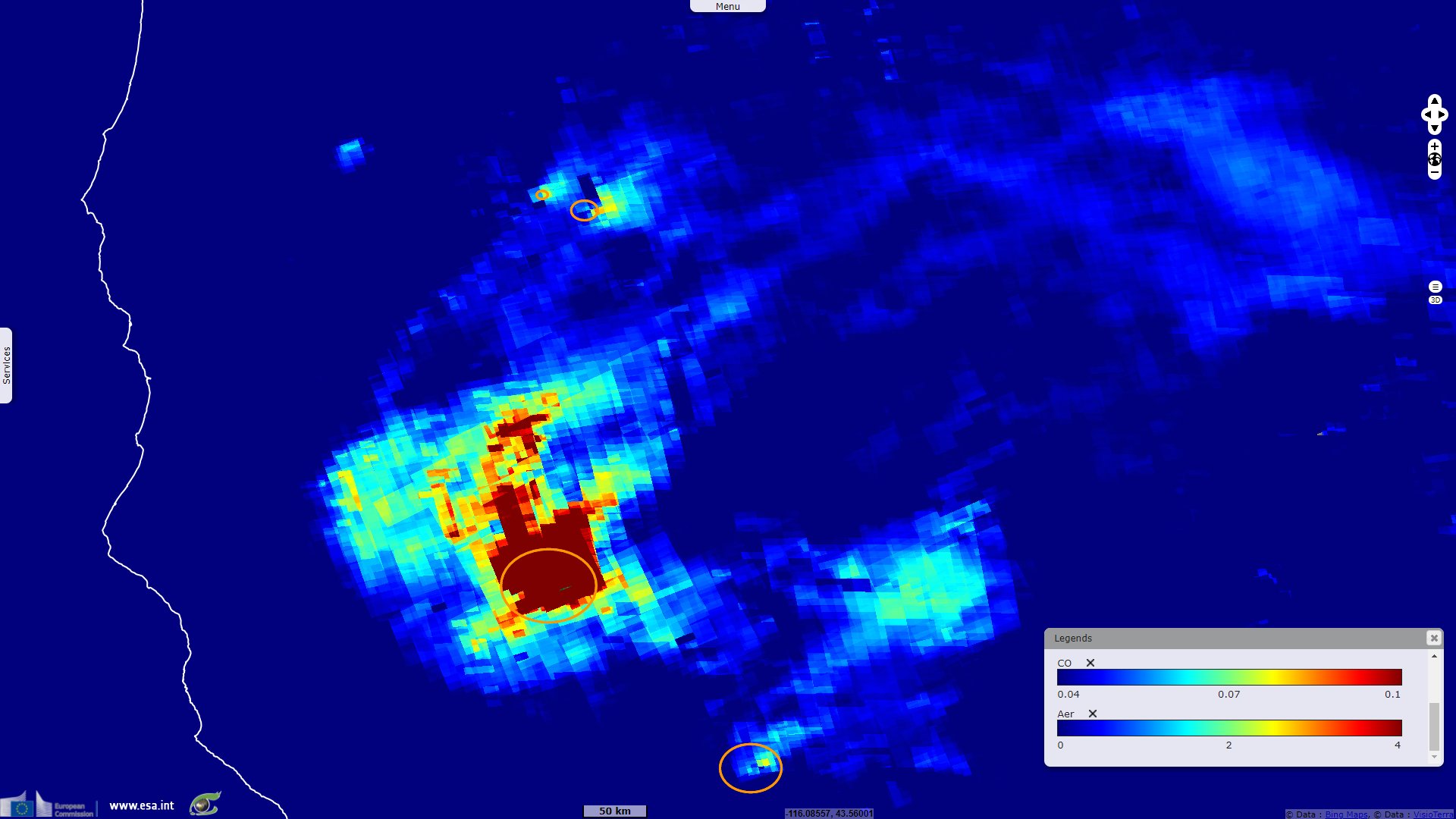
Sentinel-5P TROPOMI AER_AI & CO acquired on 22 July 2021 at 20:53:33 UTC
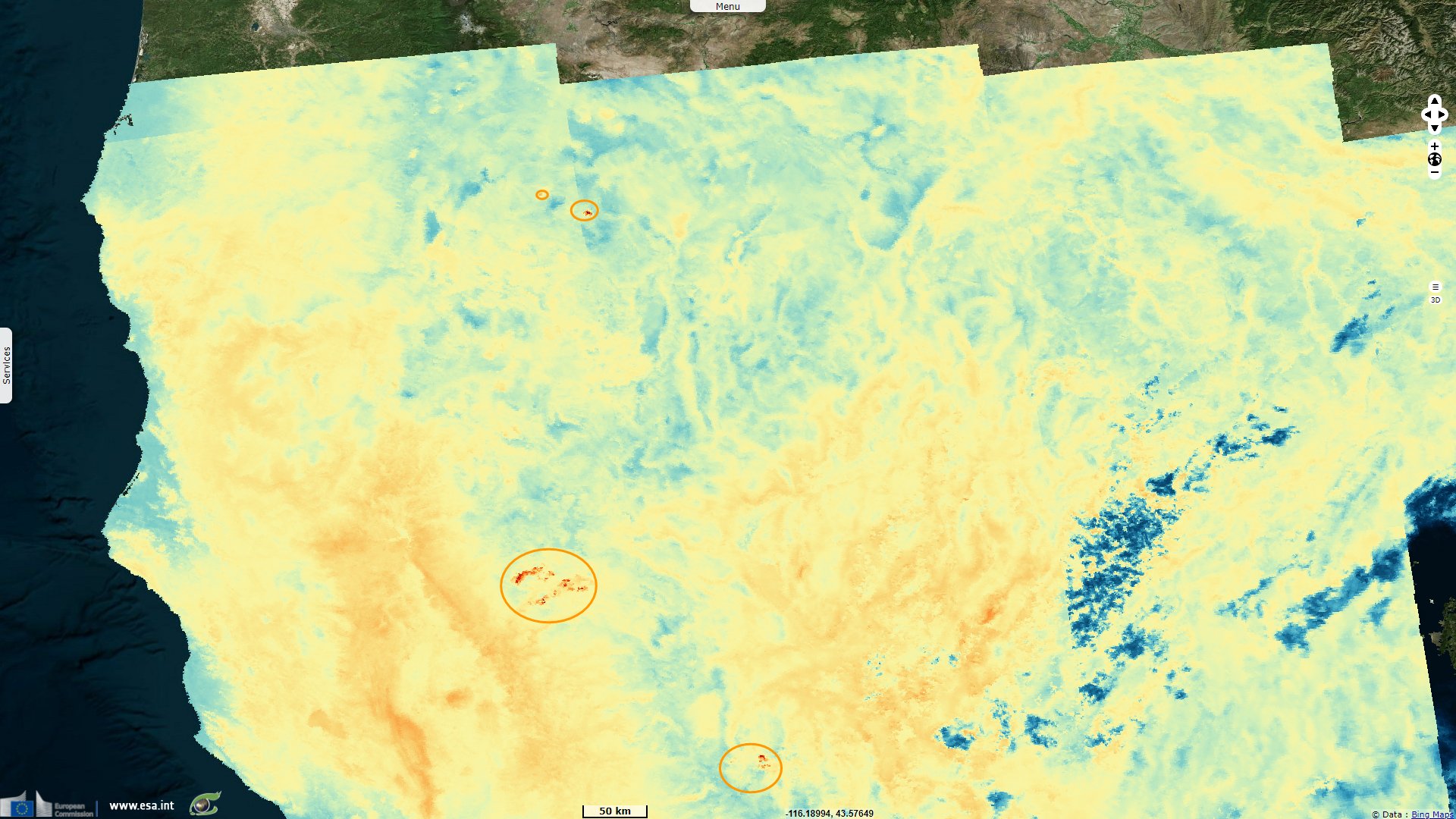
Sentinel-3 SLSTR LST acquired on 22 July 2021 at 05:54:20 UTC
...
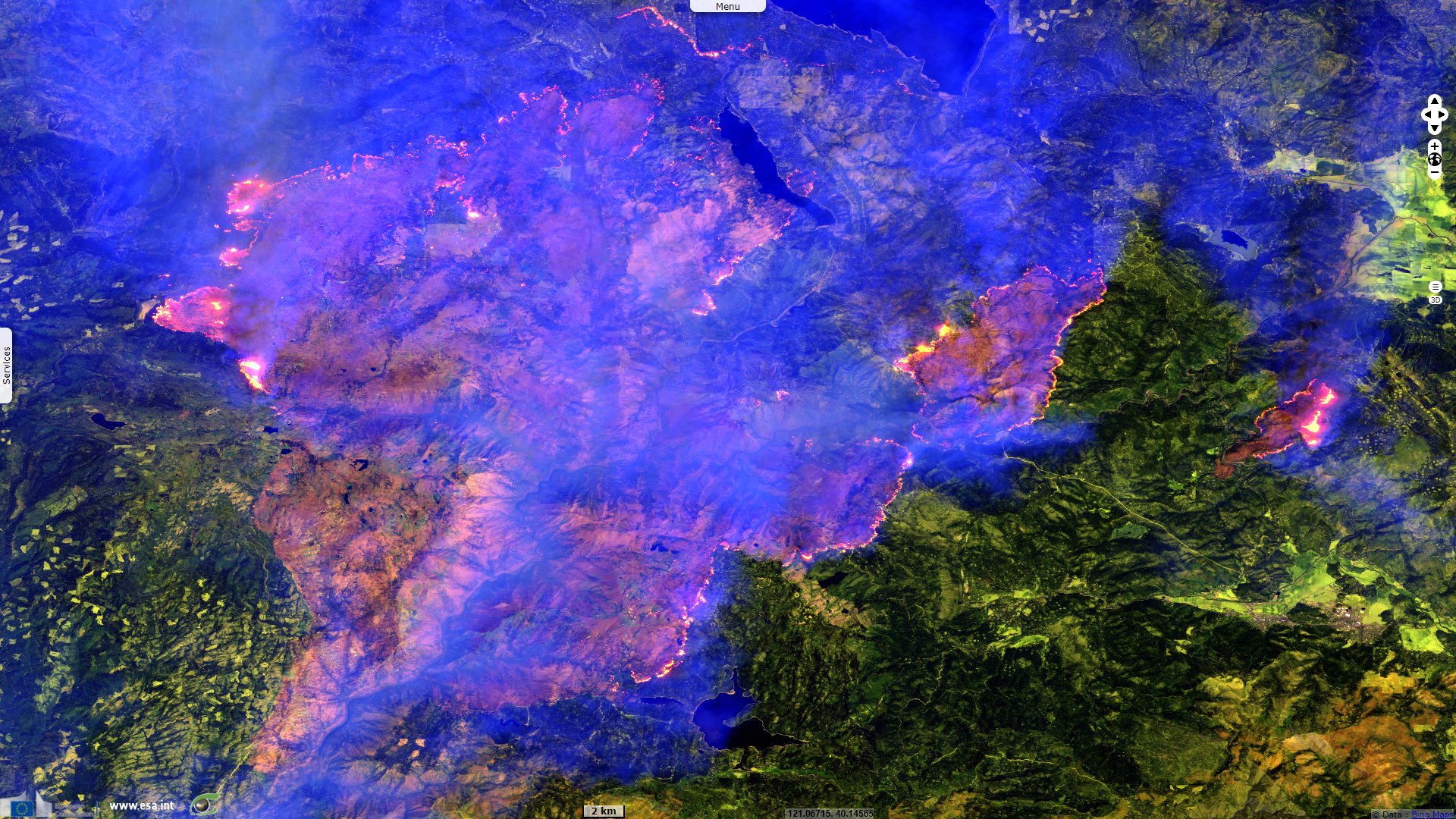
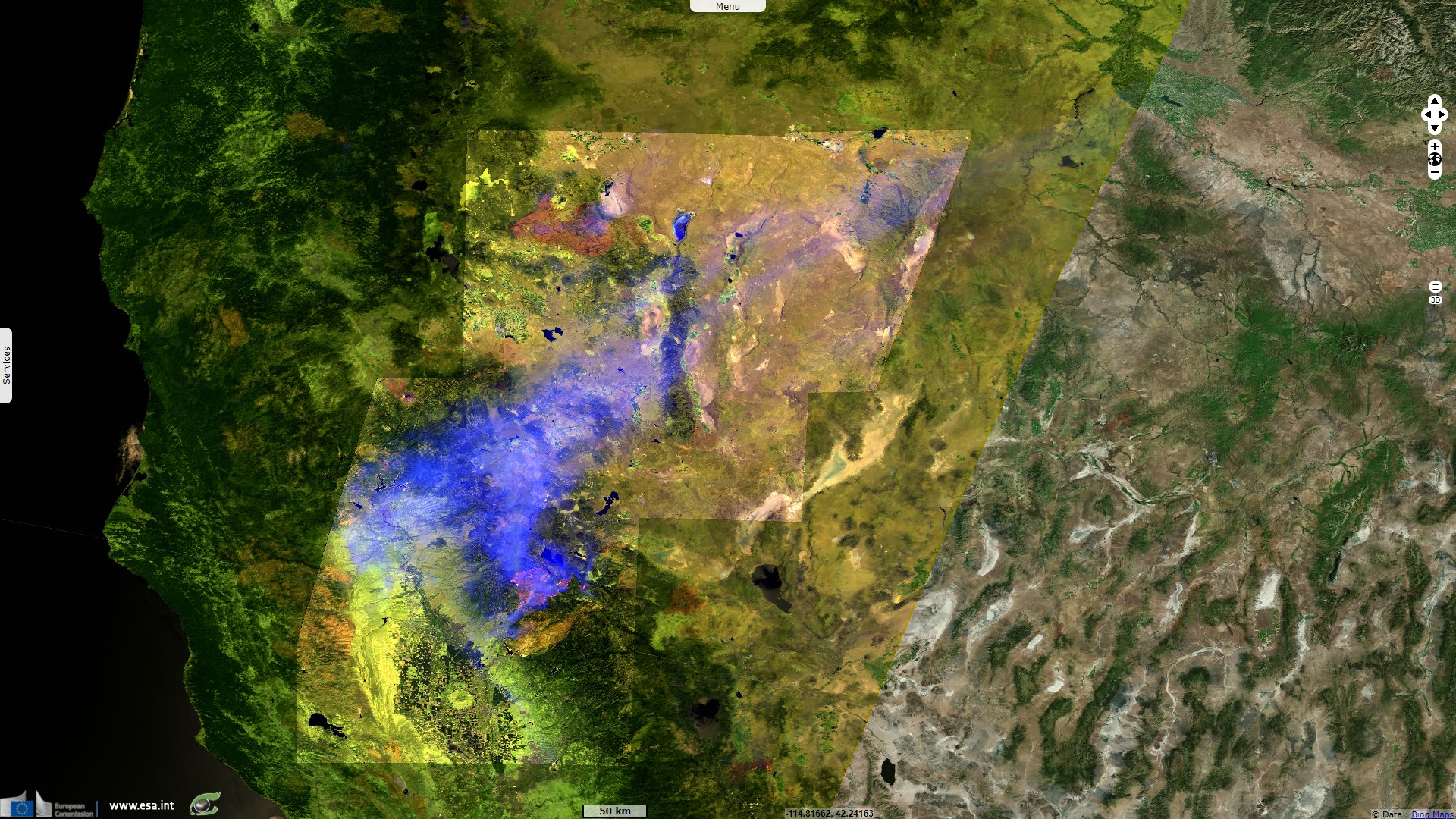
Sentinel-2 MSI acquired on 23 July 2021 at 18:49:19 UTC
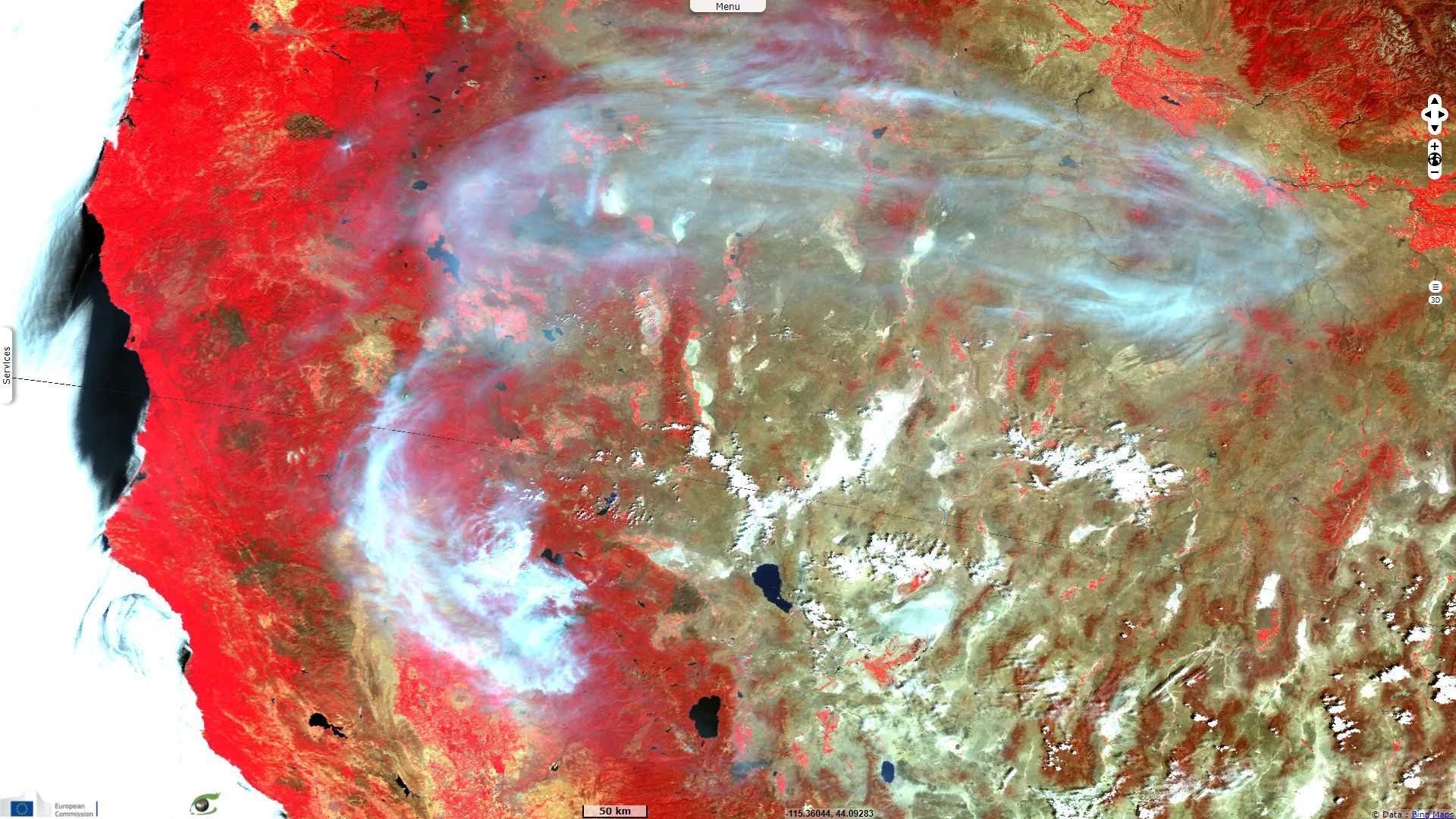
Sentinel-3 OLCI FR & SLSTR RBT acquired on 25 July 2021 from 18:30:40 to 18:33:40 UTC
Sentinel-3 SLSTR LST acquired on 22 July 2021 at 05:54:20 UTC
...
Sentinel-2 MSI acquired on 23 July 2021 at 18:49:19 UTC
Sentinel-3 OLCI FR & SLSTR RBT acquired on 25 July 2021 from 18:30:40 to 18:33:40 UTC
Keyword(s): Atmosphere, air quality, wildfires, emergency, climate change, global warming, drought, forestry, California, USA