Protected wetlands of the Gambian lifestream
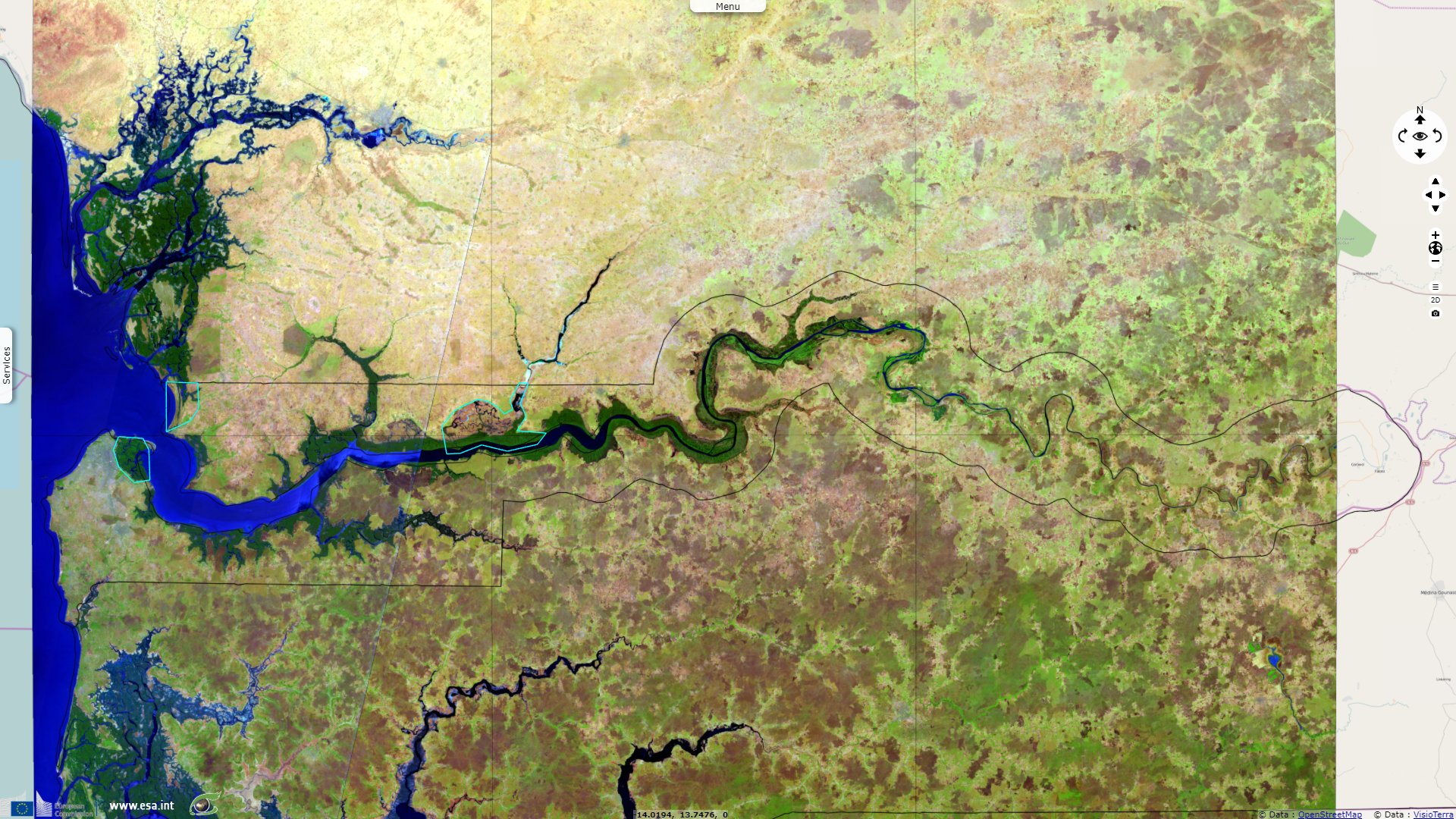
Sentinel-2 MSI acquired on 29 November 2019 at 11:33:29 UTC
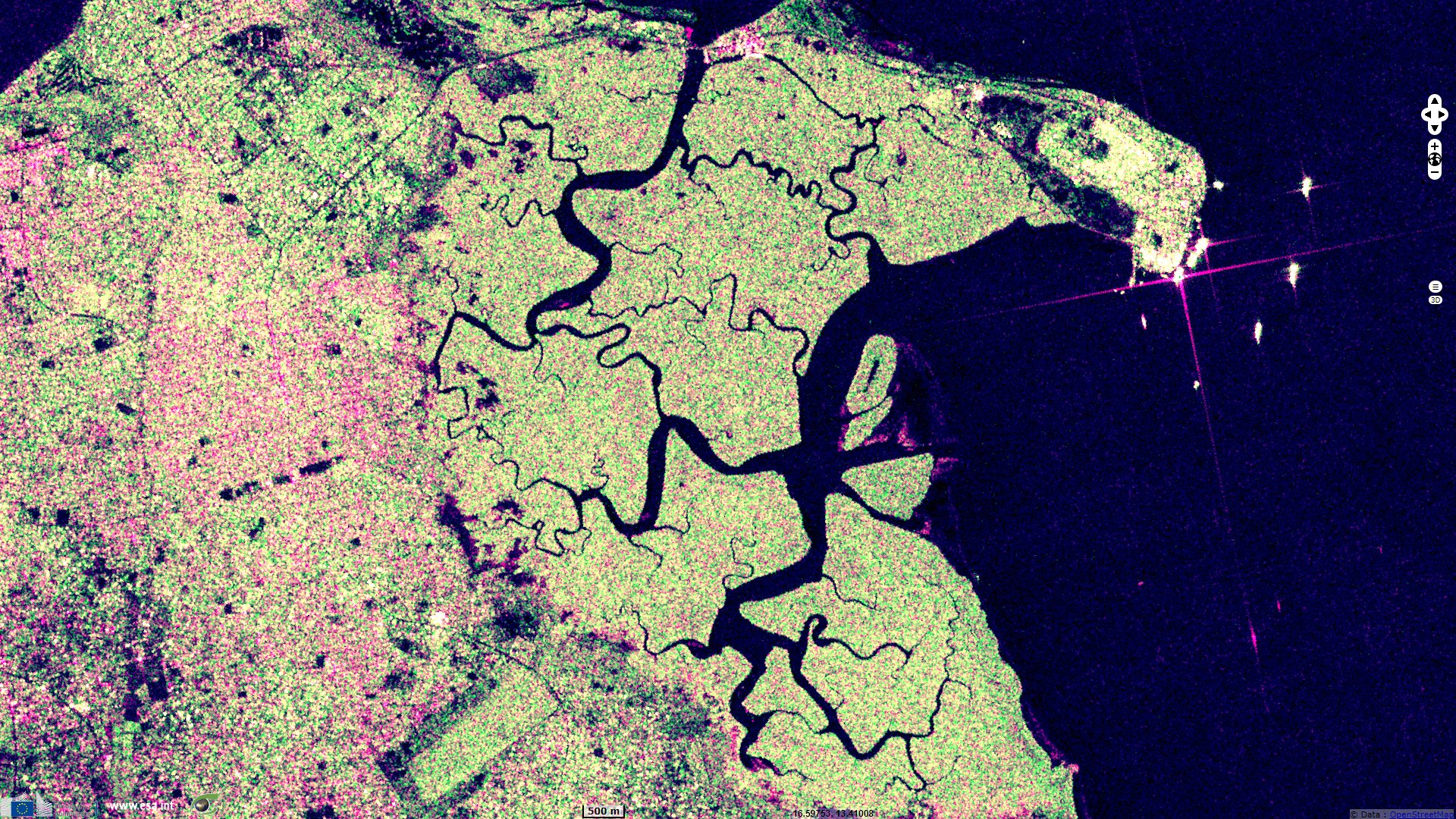
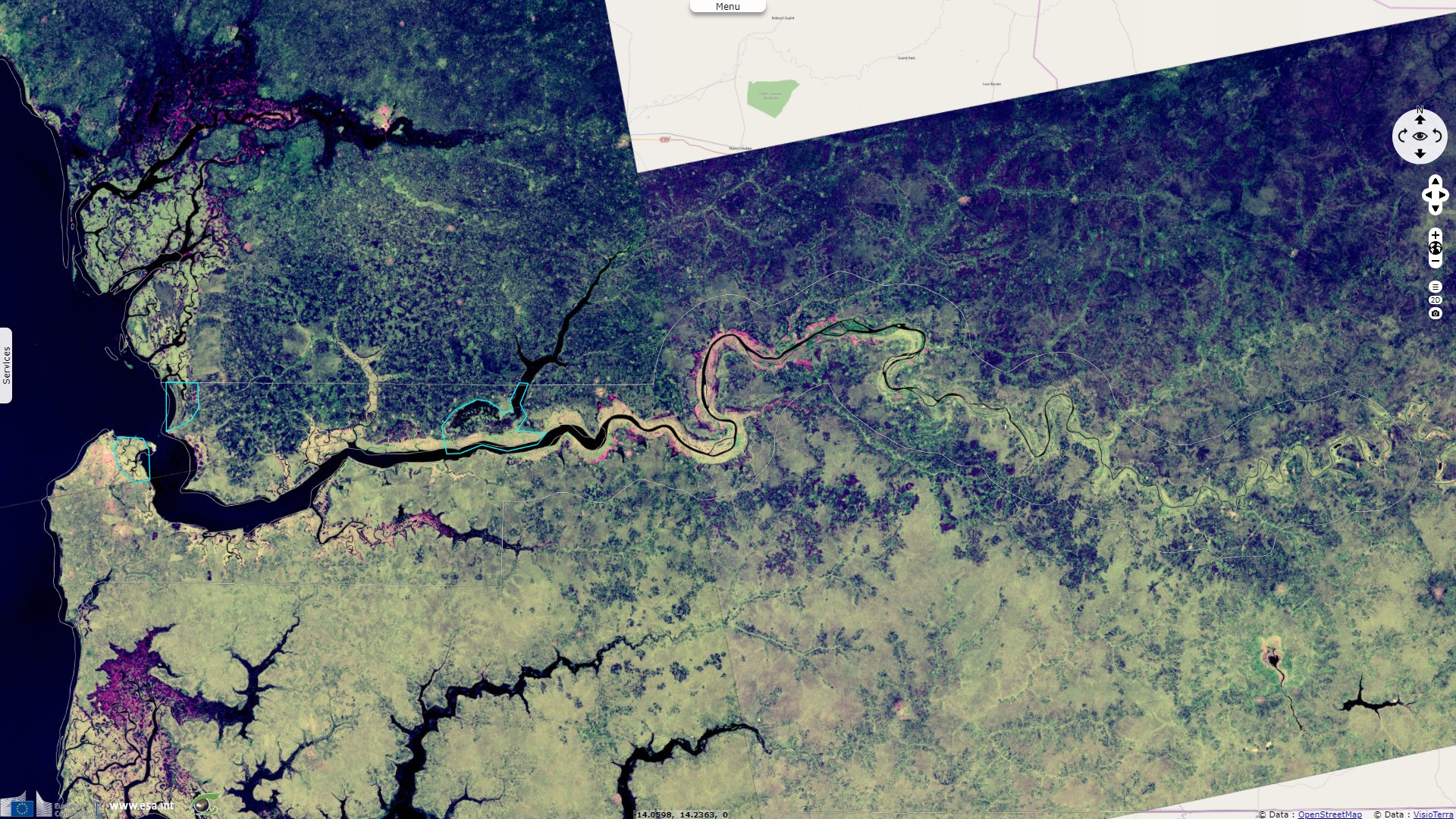
Sentinel-1 CSAR IW acquired on 29 November 2019 from 19:17:35 to 19:18:00 UTC
...
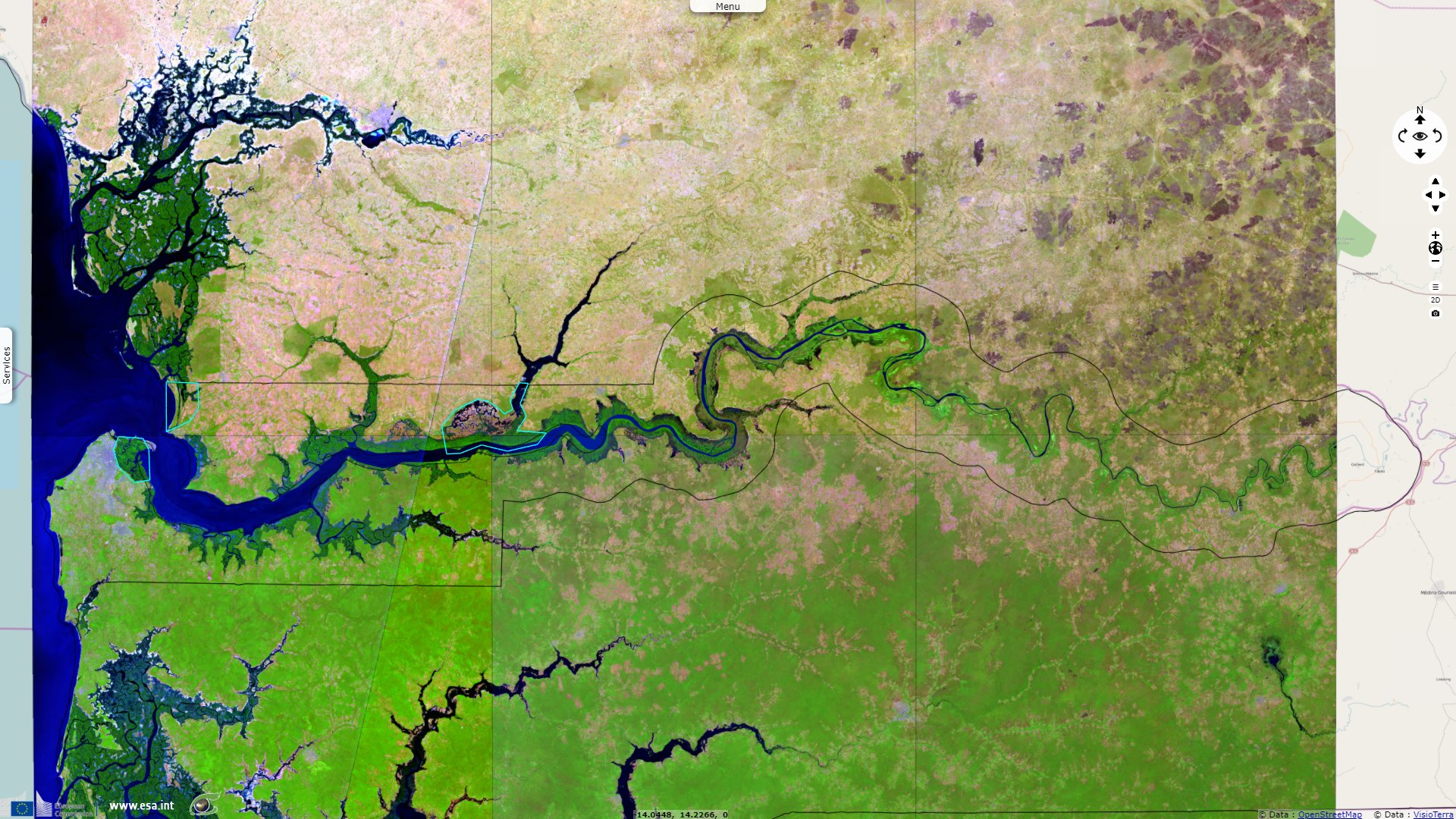
Sentinel-2 MSI acquired on 24 May 2020 at 11:21:19 UTC
Sentinel-1 CSAR IW acquired on 27 May 2020 from 19:17:35 to 19:18:00 UTC
Sentinel-1 CSAR IW acquired on 29 November 2019 from 19:17:35 to 19:18:00 UTC
...
Sentinel-2 MSI acquired on 24 May 2020 at 11:21:19 UTC
Sentinel-1 CSAR IW acquired on 27 May 2020 from 19:17:35 to 19:18:00 UTC
Keyword(s): River, Ramsar wetland, national park, mangrove, savannah, seasons, forestry, Gambia, Senegal
The Gambia is Africa’s smallest nonisland country. It is also one of Africa’s most densely populated countries. It is surrounded by Senegal, except for its western coast on the Atlantic Ocean. It is centered around the Gambia river, forming a buffer no larger than 25km. With its highest point under 60m, it is also the world's lowest nonisland country.
It has a tropical climate It is mostly covered by mangrove forest around the brackish Gambia banks that forms a ribbon around the lower watercourse. Savannah lies on the uplands.
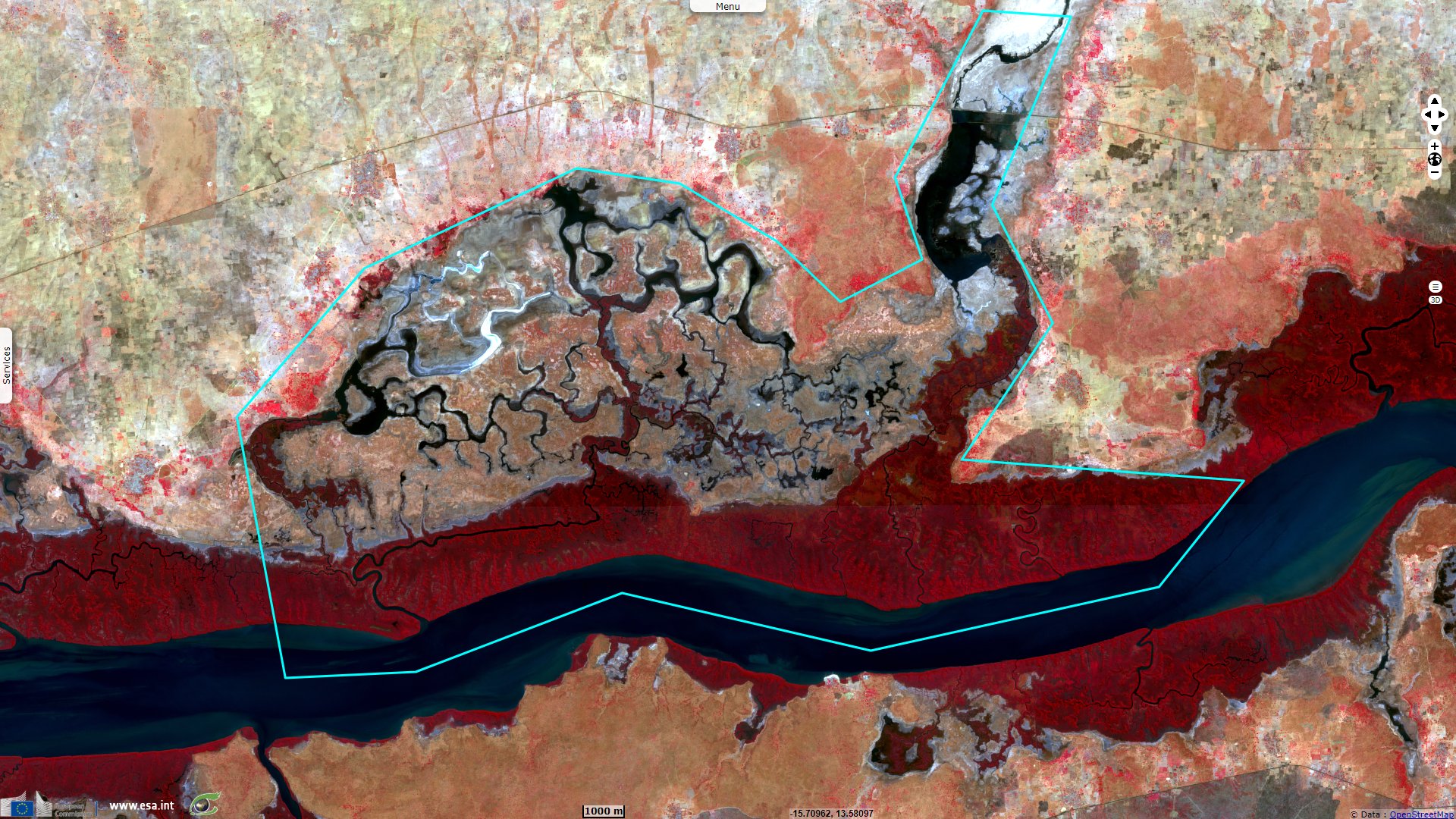
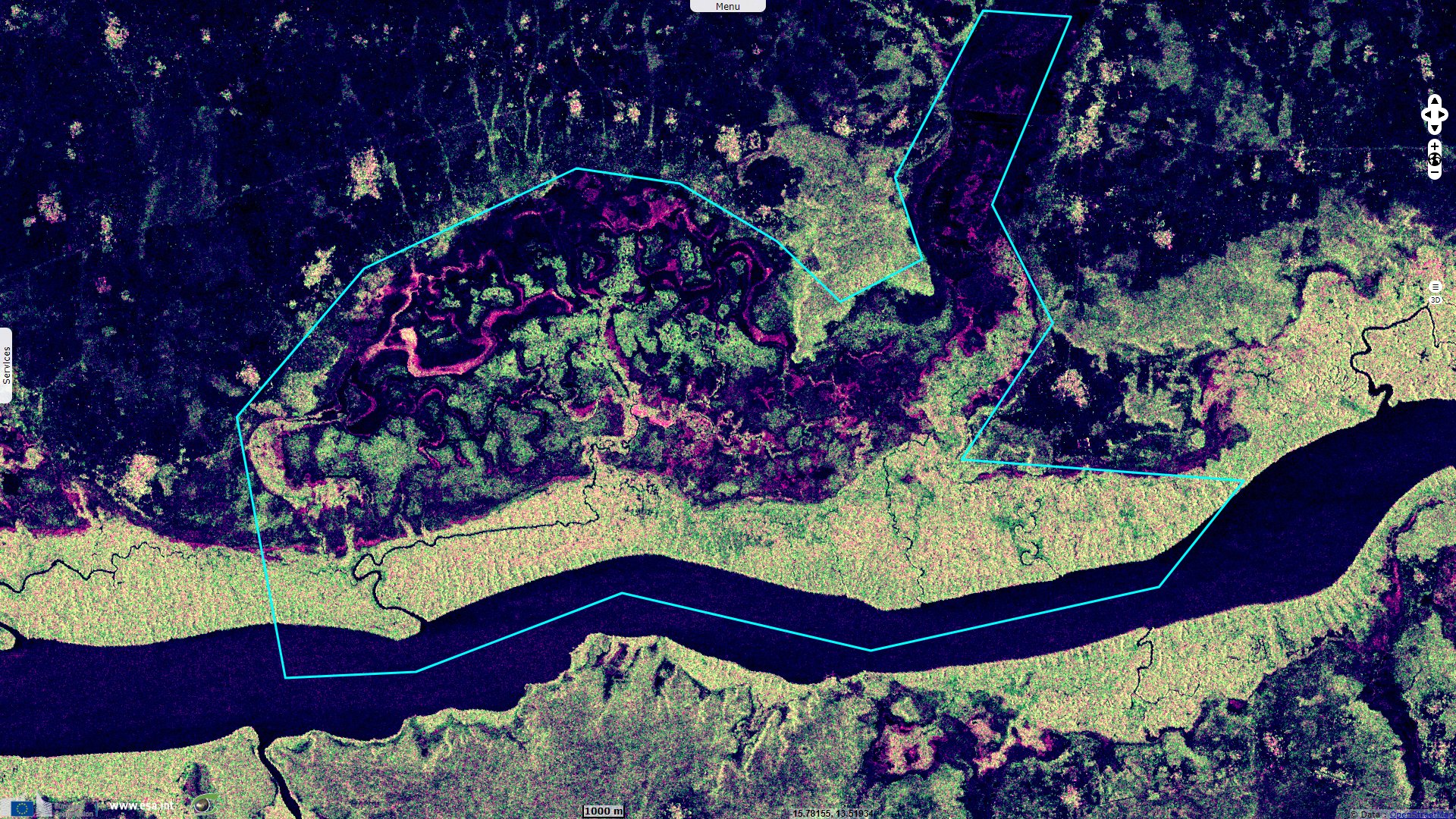
Baobolon Wetland Reserve encompasses sevral biomes. A Ramsar protected area, it is described as being "A tidal wetland complex on the Gambia River consisting of six major bolons (tributaries), tidal estuaries, and three distinct wetland ecosystems: mangrove forest, saltmarsh and savanna woodland. The tidal flats have been dyked for fresh water retention and rice production. The mangroves provide important fish spawning habitat."
Being more remote to coastal cities than the other protected wetlands of Gambia, it is also more undisturbed: "Human activities are predominantly recreational (birdwatching, wildlife viewing, fishing, and canoeing) and also include mangrove and thatch grass harvesting."
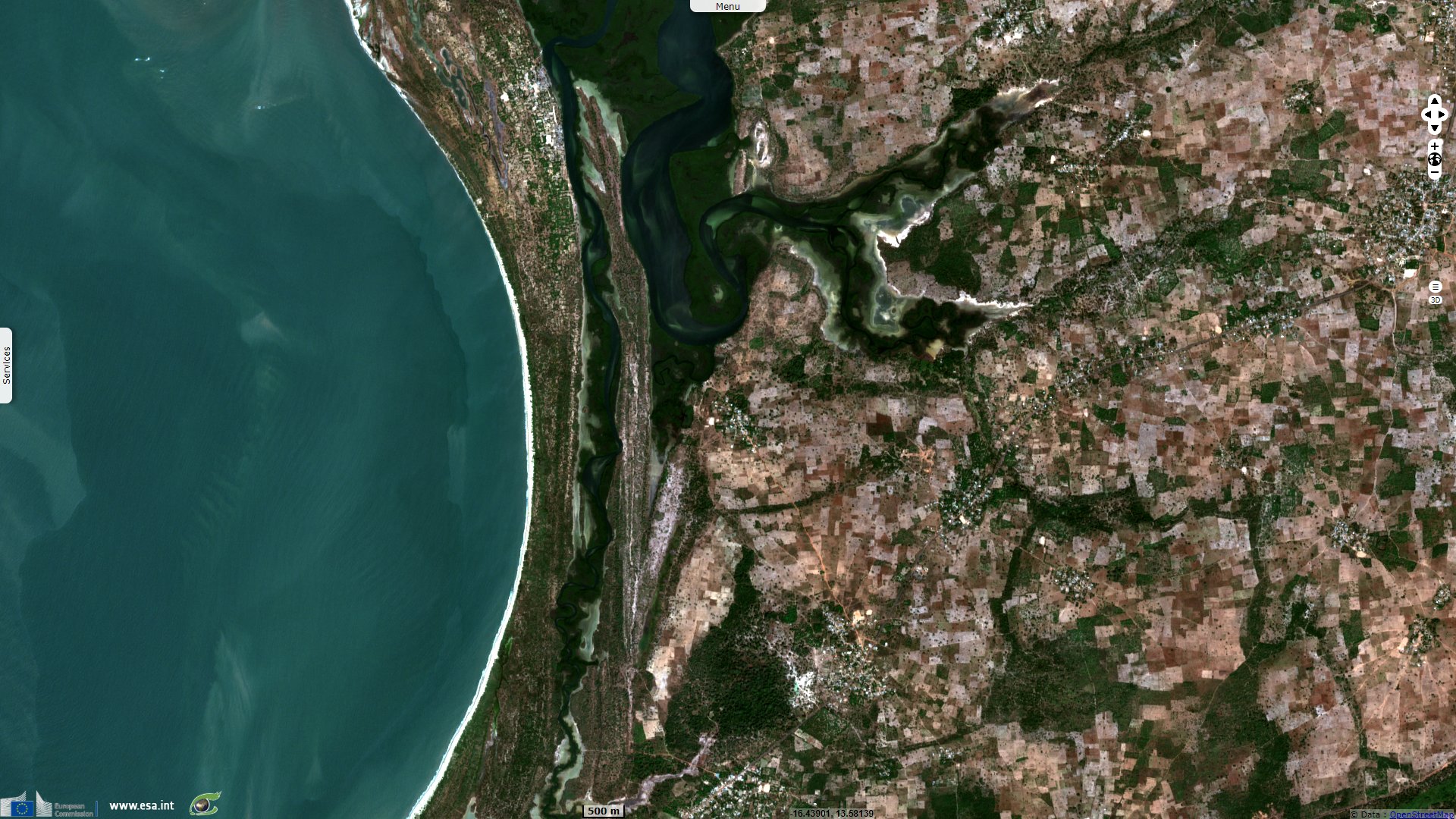
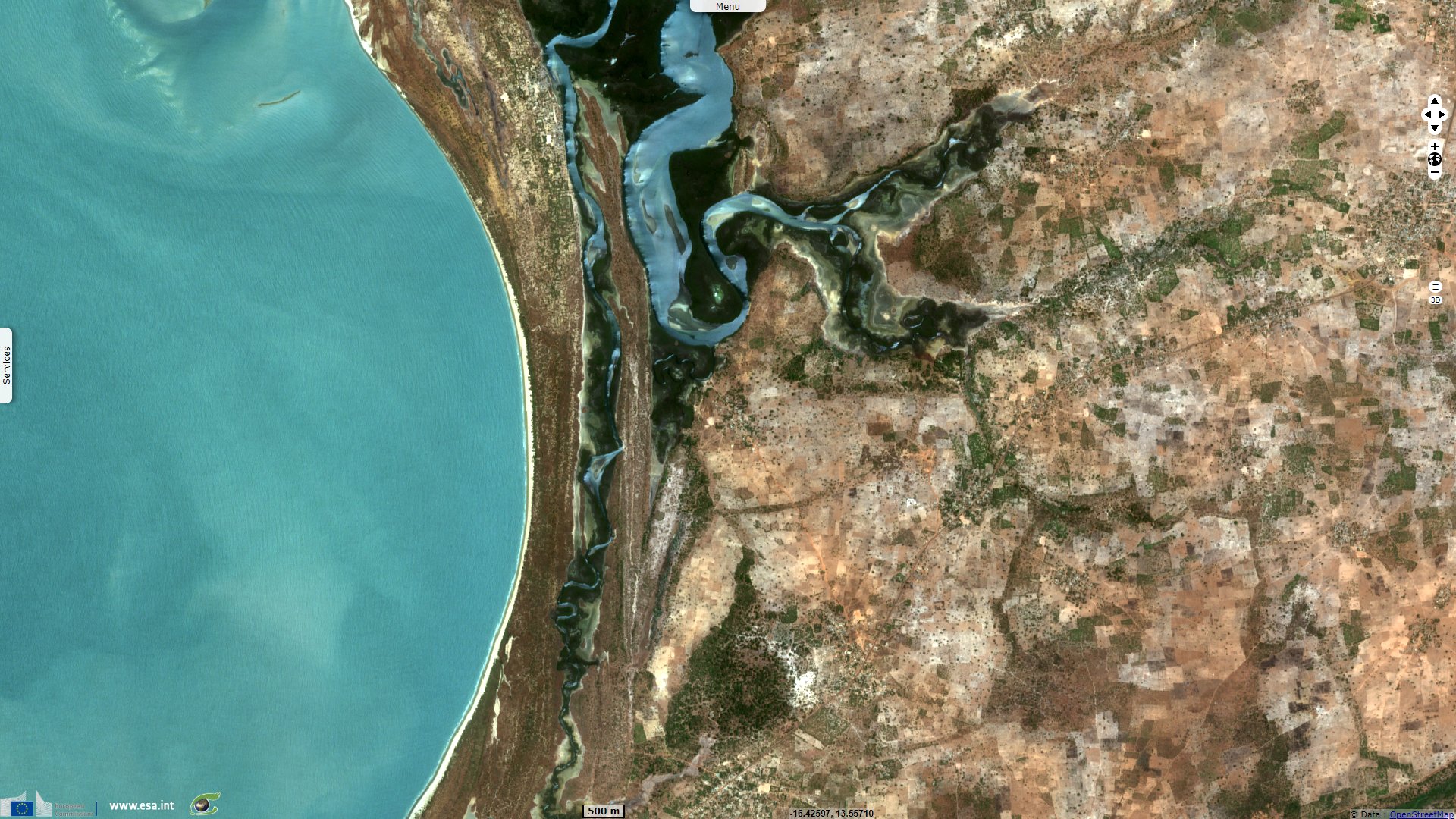
Niumi National Park is "a complex of wetland types along the coastal strip of the northern section of the River Gambia, ranging from coastal to inland wetlands which hold important hydrological values, i.e. flood control, groundwater replenishment, shoreline stabilization and sediment and nutrient retention and export. The flora and fauna are of particular note due to their abundance and adaptations to the range of habitat types found within the site. The noteworthy flora include Rhizophora mangrove forest, Nymphaea lotus, Parkia biglobosa etc. – noteworthy fauna include 303 species of resident and migratory birds, the West African manatee, leopards, and Red Colobus monkeys" says its Ramsar sheet.
Its proximity to a larger population than was Baobolon Reserve makes it more affected by human activities: "Human uses within the site are noted as rice cultivation, livestock rearing, and fishing activities. In the surrounding areas some small industries are in operation. Potential threats are due to unsuitable fishing practices, illegal hunting, land clearance, expansion of agricultural activity, and sand mining."
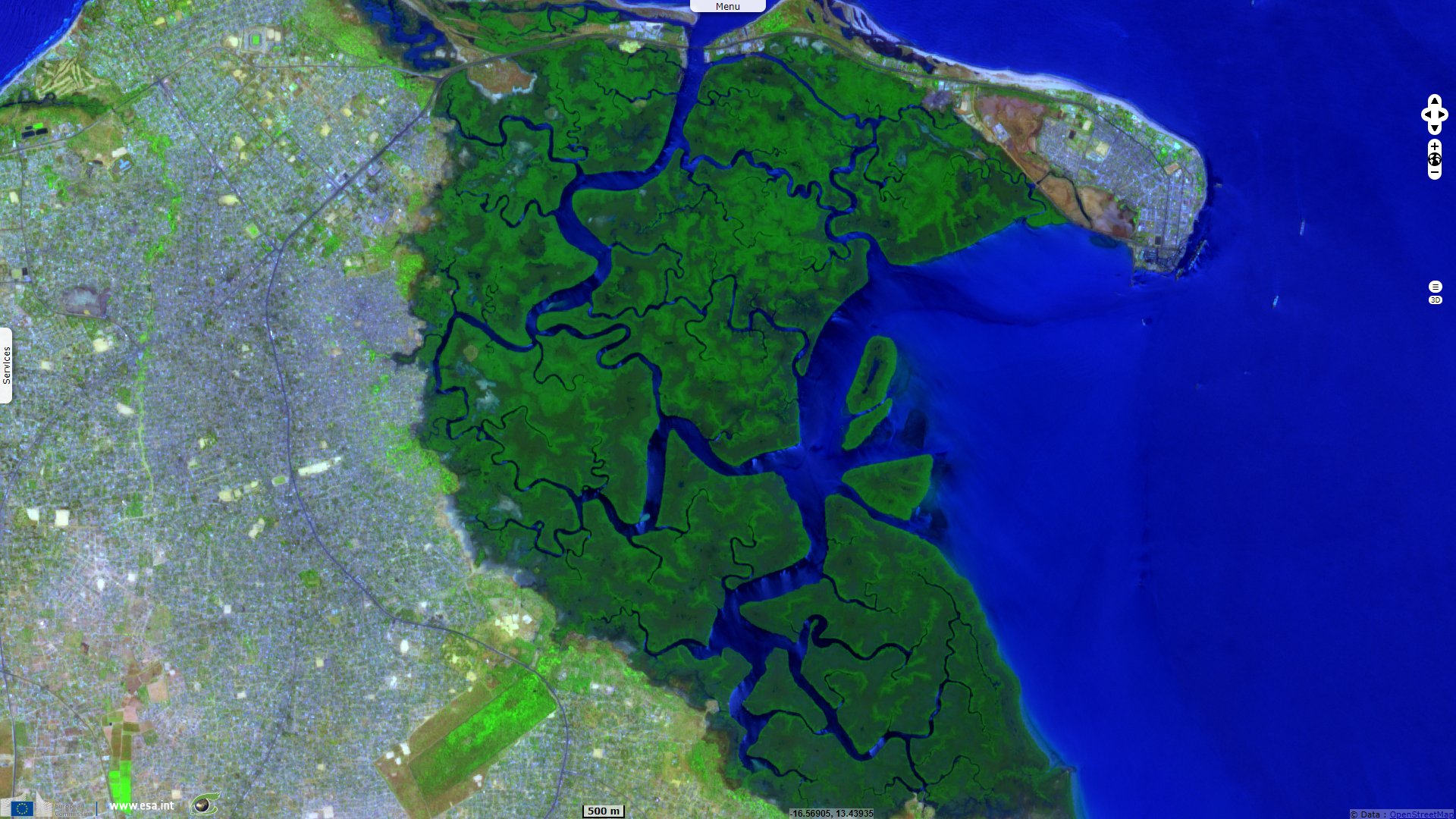
Located at the mouth of river Gambia with the Atlantic on its southern bank, Tanbi National Park lies "A low-altitude zone formed from the deposition of marine and fluvial sediments, which constitutes estuarine and intertidal forested wetlands, 80% of which is dominated by mangrove swamps. It captures incoming water and rainfall, thus playing an important role in shoreline stabilization, sediment and nutrient retention and export, ground water replenishment and flood control, thereby acting as a hydrological buffer zone. This site harbours vulnerable species like the African manatee, African Clawless otter and the Western Red Colobus. The shade of the mangroves provide an important breeding ground for the shrimp Panaeus notialis in the Western African Marine Eco-region." according to its description.
The surrounding land area has been urbanized on all sides, it is then the most exposed to anthropic pressure: "Activities carried out in this area include subsistence fishing and agriculture, oyster and mangrove harvesting and tourism. Exposure to negative influences such as rapid coastal erosion, industrialization and agriculture has been noted."