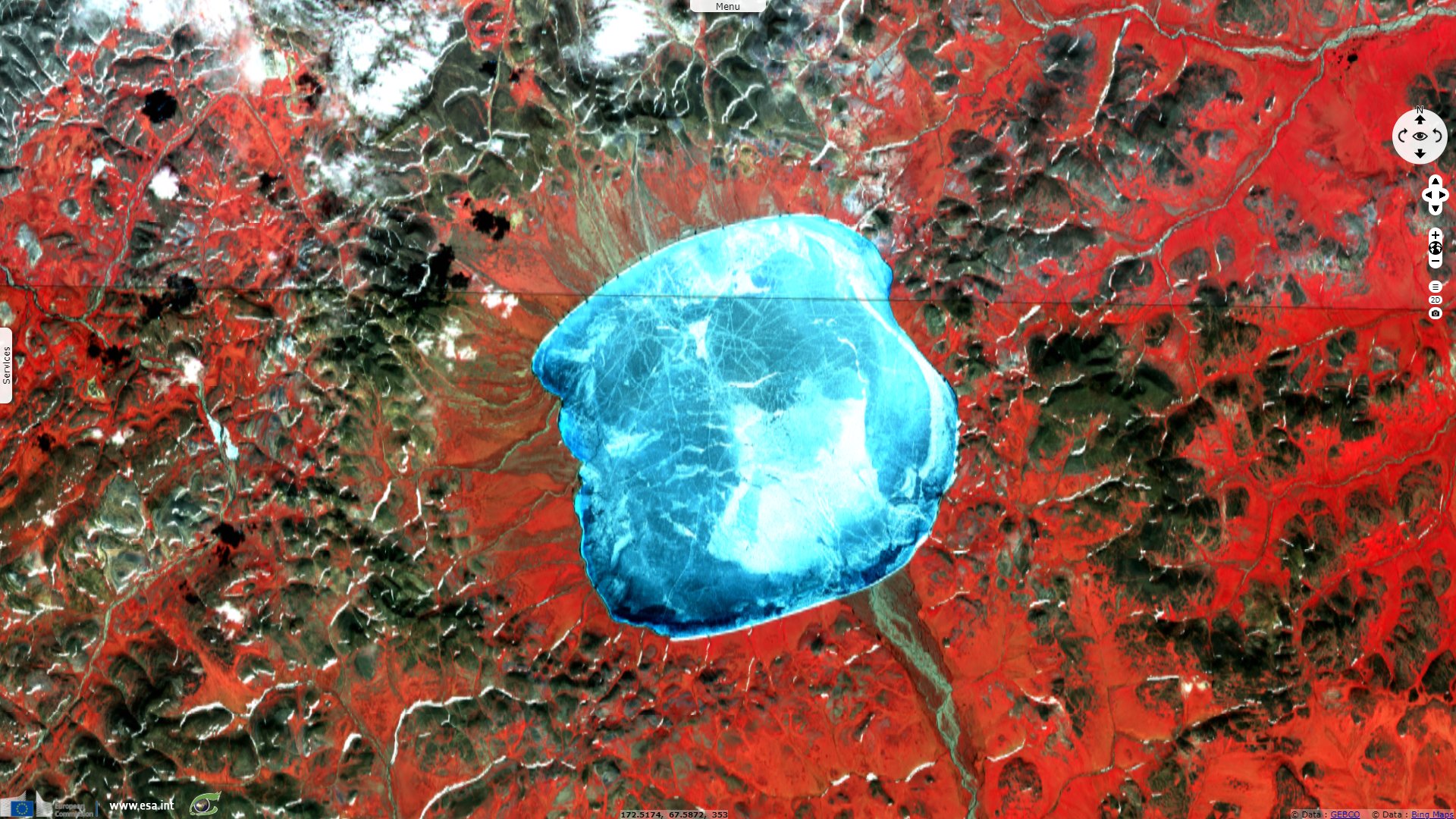
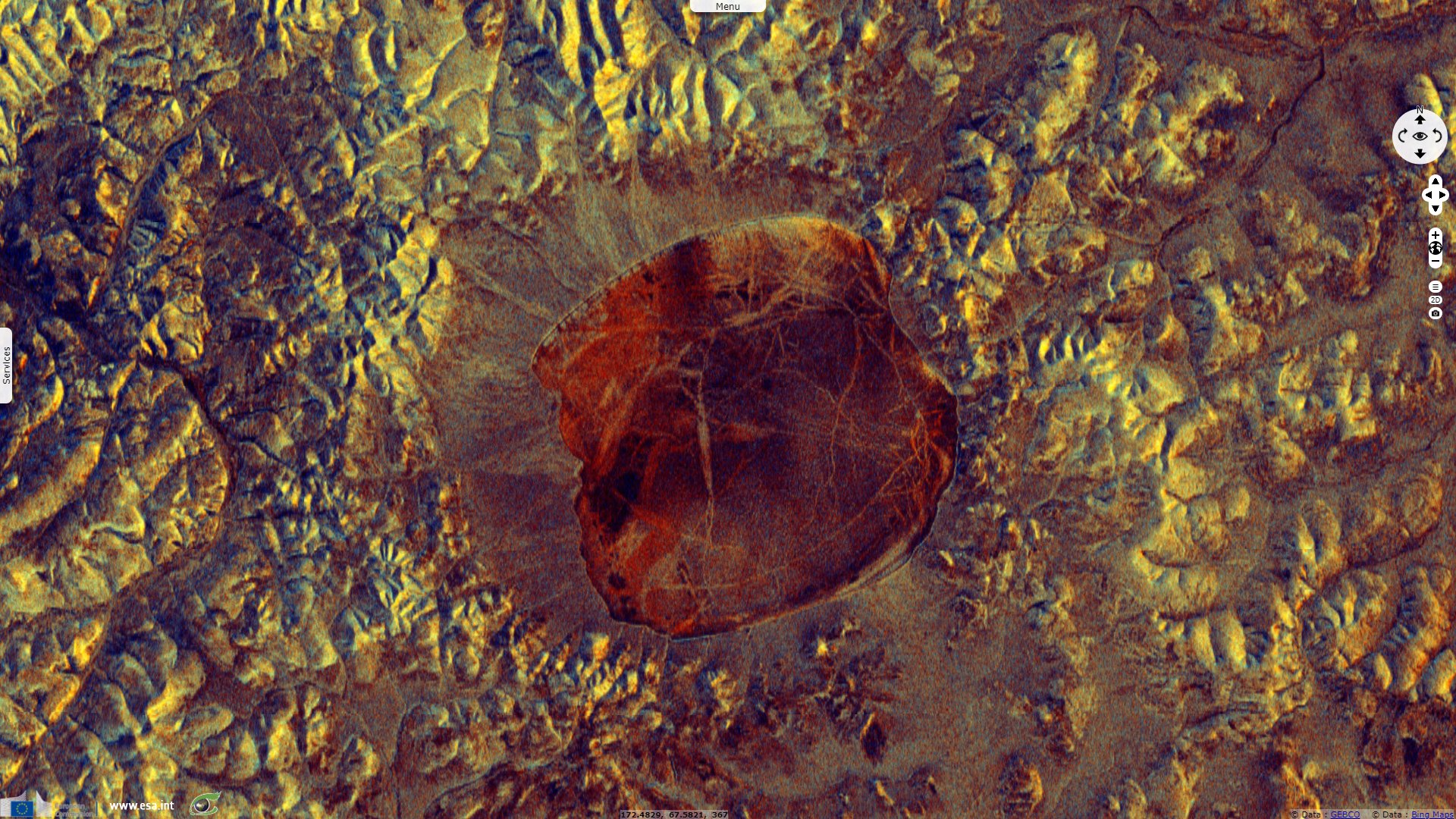
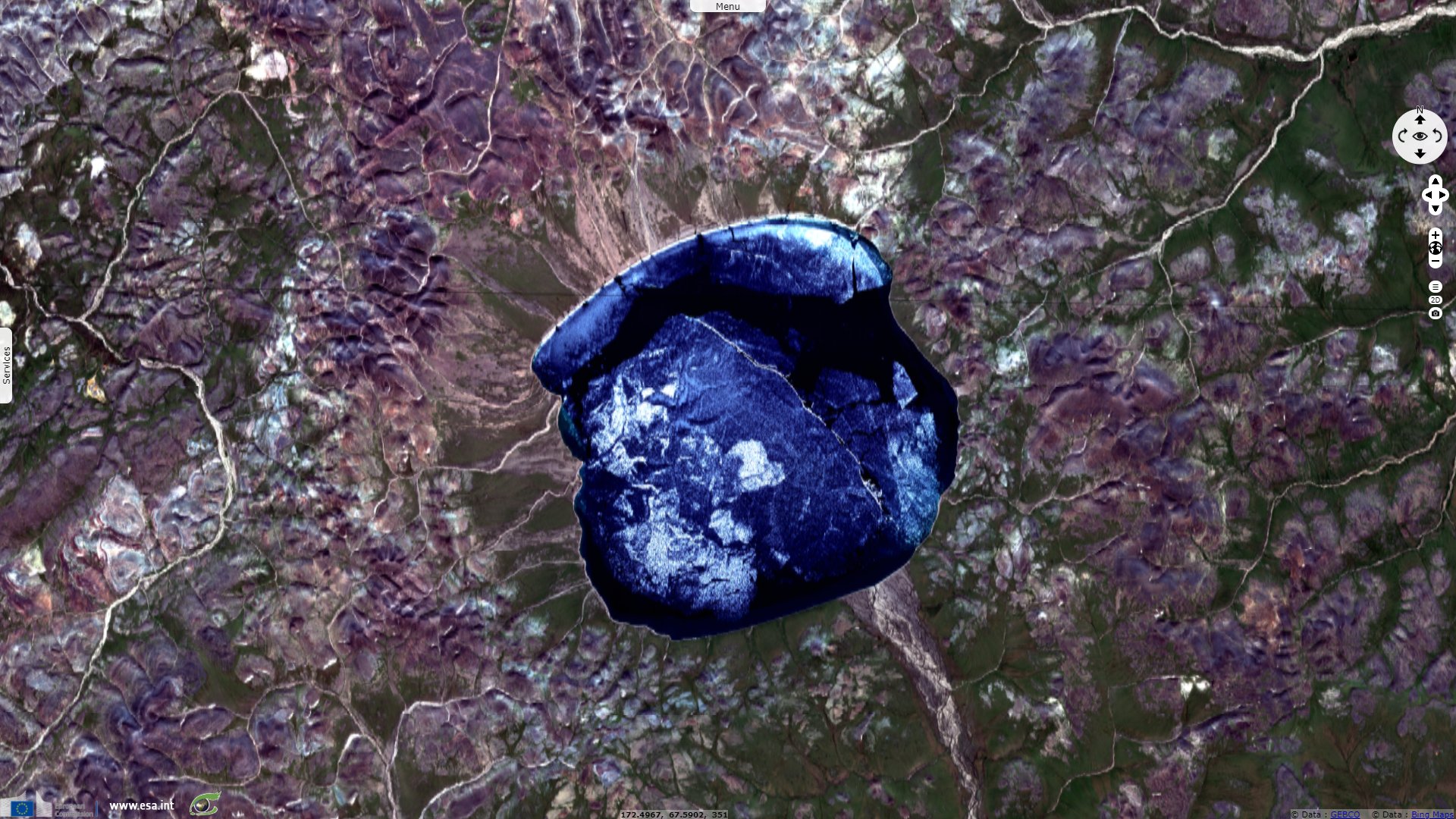
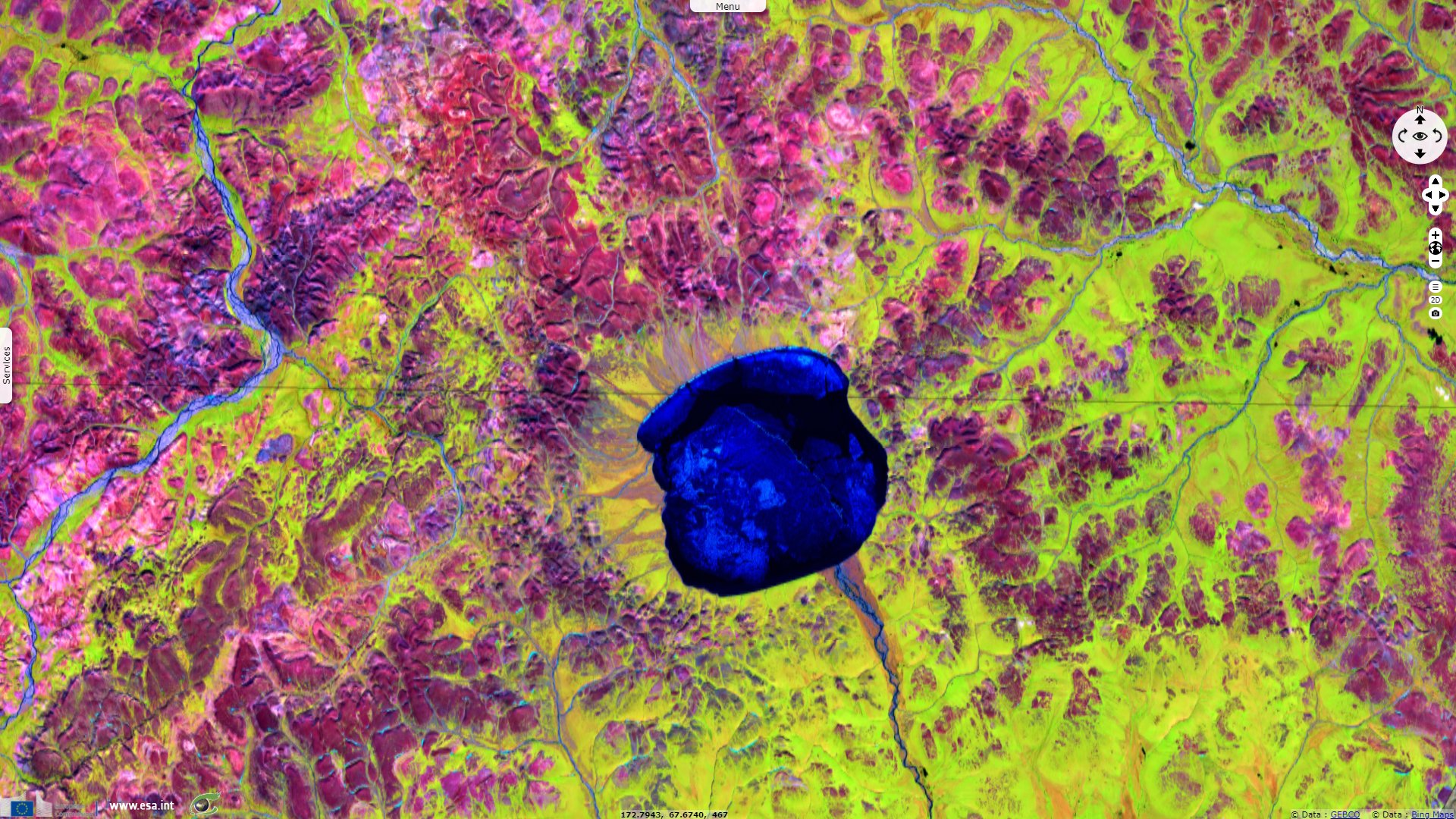
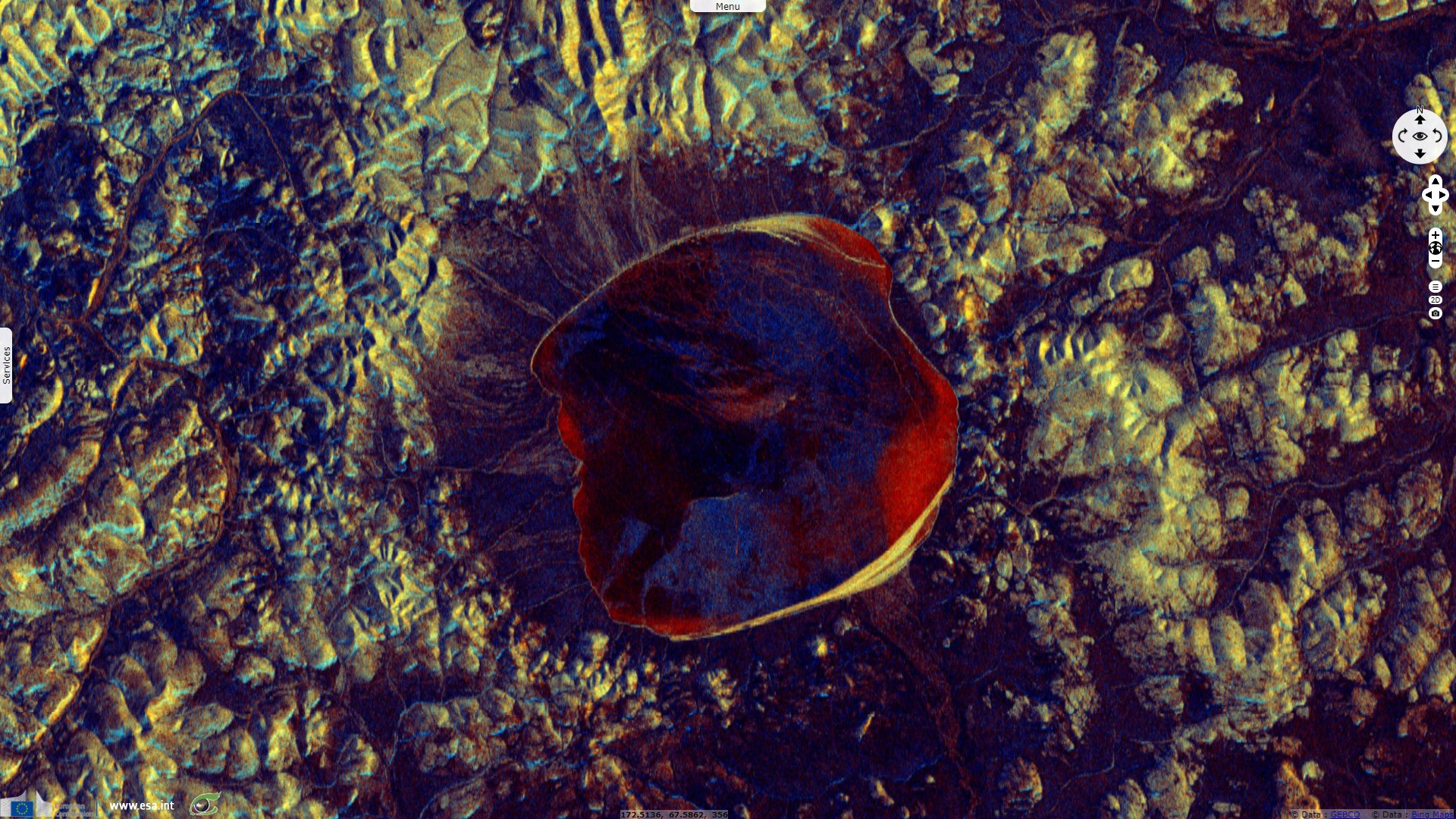
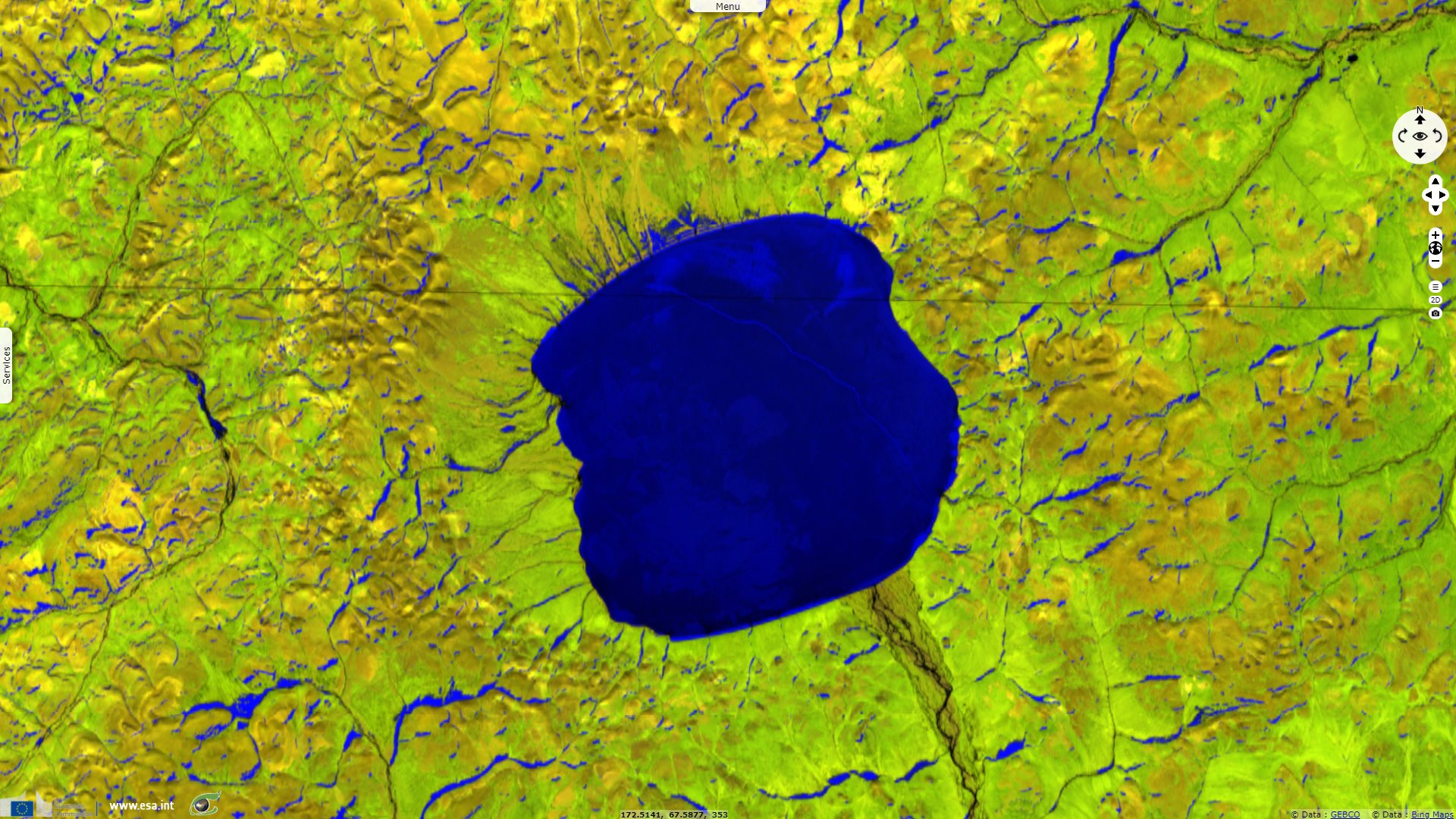
Lake Elgygytgyn, north-east Russia
Sentinel-2 MSI acquired on 17 June 2016 at 00:36:12 UTC
Sentinel-2 MSI acquired on 16 June 2019 at 00:16:11 UTC
Sentinel-2 MSI acquired on 12 July 2019 at 00:36:11 UTC
Sentinel-1 CSAR IW acquired on 04 December 2019 at 19:03:13 UTC
Sentinel-1 CSAR IW acquired on 20 May 2020 at 19:03:13 UTC
Sentinel-2 MSI acquired on 16 June 2019 at 00:16:11 UTC
Sentinel-2 MSI acquired on 12 July 2019 at 00:36:11 UTC
Sentinel-1 CSAR IW acquired on 04 December 2019 at 19:03:13 UTC
Sentinel-1 CSAR IW acquired on 20 May 2020 at 19:03:13 UTC
Keyword(s): Crater lake, polar, cryosphere, climate change, Siberia, Russia
Fish species in the lake are adapted to its very cold waters, which are generally just above the freezing point, and spend most of the year in total darkness. The surface is frozen for about 10 months of the year. It may start to melt in the summer, but some years it never fully thaws.
This has allowed the uninterrupted build-up of 400 m of sediment at the bottom of the lake, recording information on prehistoric climate change.